










ỉP`«—nu
MẨU NHÃN HÔP & LỌ
Sãn phẩm : Thuốc Tiêm SCUBIG
vj[lt 'ch thước hộp : 70 x 45 x 35 mm
Kĩch thước lọ : 80 x 30 mm
omnas ỉ ~
1 Nội dung : như mẫu
——ỨỂ—… ù
iẮPrasctlptiondnn ) ……MuựỳMmmmm Ế Bunm
› o Comositton: Each vial oontainsl Ị 0 M phia: Mờ lo chia
Cetoxttin SOđIWTI ' W …
' (equ'vaient to Cetuxitin tq)
) Ị mm … cmmn to)
) O Imiintions. ndmlnistntlon. i . … qm_ ddt ỦỜM. ỦỦII
) eontnimiiutinm: } di m: Xin doc trong n
See insert paper [ MM dkt sủ dutq.
\ Cefoxỉtin 1 g ° W…- ln ² hỂỆm WMfặ Cefoxitin 1 g i. … ủ mm mp .… …, mo
i d Ia below a ot ct tro . ' '
' IndeIủion "ẫymp ce m e m Thưỉc tiem (tm) i TỂẵ T: Ĩgcb ư W-
T _ . ' ` Q 3 . ,
l . Packue. iglvìal. 1 ' Ị ỉl'htốc tiêm truyén |
\ 1 06 xa tãm tay trò cm
\ \ Keep ou d reach a mm… ! i _ .
4 mm insert papemrutưy betoretsino ' ZĨwkỸ "Mũanffldwmm
ủ PHIL mưa pm… Sán má …
/"\_/ ……mm
sơtosx 20.HmNam.ktum
nsx. ViOt Nun - Singapore.
un
. ;… ,J-- _; 1ỂL p\
, của TY ’
Tị~ii—'H
FIĨ’L ’ì'Ĩì`aÊR
' ' Ặõftoxiẵậhts’tẳd/uEnach vi:! uontairis
Iniedlm/Inftmon . ,
(… Ủllll GIÍDXI 1
Cefoxitỉn 1g ° '" “’
MuomcumnmmuMn CTYTIMHILMEIIMU
SĐK:
Số 10 SX'
NSX
HD:
!]
JIF pÁmrÁo CHẤT LƯỢNG
\ẹnmrm SƯỚNG LAN
n~—Ộ
Rx Thuốc bán theo đơn
Để xa tầm tay trẻ em
Đọc kỹ hướng dẫn sử dụng trước khi dùng
Nếu cẩn thêm thông tin, xin hỏi ý kiến bác sĩ
SCUBIG
SĐK: .............
THÀNH PHÀN: Mỗi lọ chứa: ,
Hqạt chât: Cefoxitin sodium tương đương Cefoxitin ............. 1 g ị)zN
DẠNG BAO CHẾ. Bột pha tiêm i
DỪỢC LỰC HỌC
Cefoxitin là một kháng sinh cephalosporin bán tổng hợp phố rộng. Tảc dụng diệt khuấn cùa
cefoxitin 1ả do ức chế tổng hợp thảnh tế bảo vi khuấn. Trên in vitro, Cefoxitin có phổ kháng
khuẩn rộng đối với cảc loải vi khuấn gram âm và gram dương. Nhóm chức methoxy gắn tại vị
trí 7u giúp cefoxitin bền vững với beta- lactamase, bao gồm cả penicillinase vả
cephalosporinase của vi khuấn gram âm.
DƯỢC ĐỘNG HỌC
5 phủt sau khi dùng đường tĩnh mạch liều 1 g, nồng độ Cefoxitin trong huyết thanh đạt được là
110 mcg/mL và giảm xuông dưới 1 mcg/mL sau 4 giờ. Thời gian bản thải sau khi dùng thuốc
theo đường tĩnh mạch là 41 — 59 phút. Có khoảng 85% cefoxitin được bải tiết qua thận dưới
dạng không biến đổi trong vòng 6 giờ, dẫn đên thuốc có nồng độ cao trong nước tiếu
Probenecid lảm chậm quá trình bải tiêt ua ống thận và lảm tăng nông độ thuốc trong huyết
thanh, kéo dải thời gian có thể đo được nông độ thuốc trong huyết thanh
Cefoxitin thâm nhập được vảo mảng phổi và dịch khớp và đạt được nồng độ có tác dụng
khảng khuẩn trong mật.
CHỈ ĐỊNH
Điều trị:
Cefoxitin được chỉ định điều trị các nhiễm khuấn nặng gây nên bởi cảc vi khuấn nhạy cảm
trong các bệnh sau:
- Nhiễm khuẩn đường hô hấp dưới bao gồm cả viêm phồi vả ảp xe phổi
— Nhiễm khuẩn đường tiết niệu
- Nhiễm khuẩn trong ô bụng bao gồm cả viêm mảng bụng và áp xe trong ổ bụng.
- Nhiễm khuấn phụ khoa bao gồm cả viêm mảng trong tử cung, viêm mô tê bảo chậu
hông và nhiễm khuấn vùng chậu hông.
— Nhiễm khuấn huyết
- Nhiễm trùng xương và khởp
- Nhiễm khuân da và cấu trúc da.
Dựphòng:
Cefoxitin được chỉ định dự phòng nhiễm khuẩn ở cảc bệnh nhân phẫu thuật đường tiêu hoá,
căt bỏ tử cung đường am đạo, cắt bỏ tử cung đường bụng hoặc dùng thủ thuật Cesar.
LIÊU LỰỢNG VÀ CÁCH DÙNG
LJE U DÙNG
Điều trị
Người Iởn
Liều thường dùng cho người lớn là 1-2g mỗi 6—8 giờ. Liều dùng cần được xác định dựa theo
vì khuân gây bệnh, mức độ nặng nhẹ cùa bệnh và thể trạng bệnh nhân (xem bảng 1).
1/6
`ĨỂ'
?
4
_
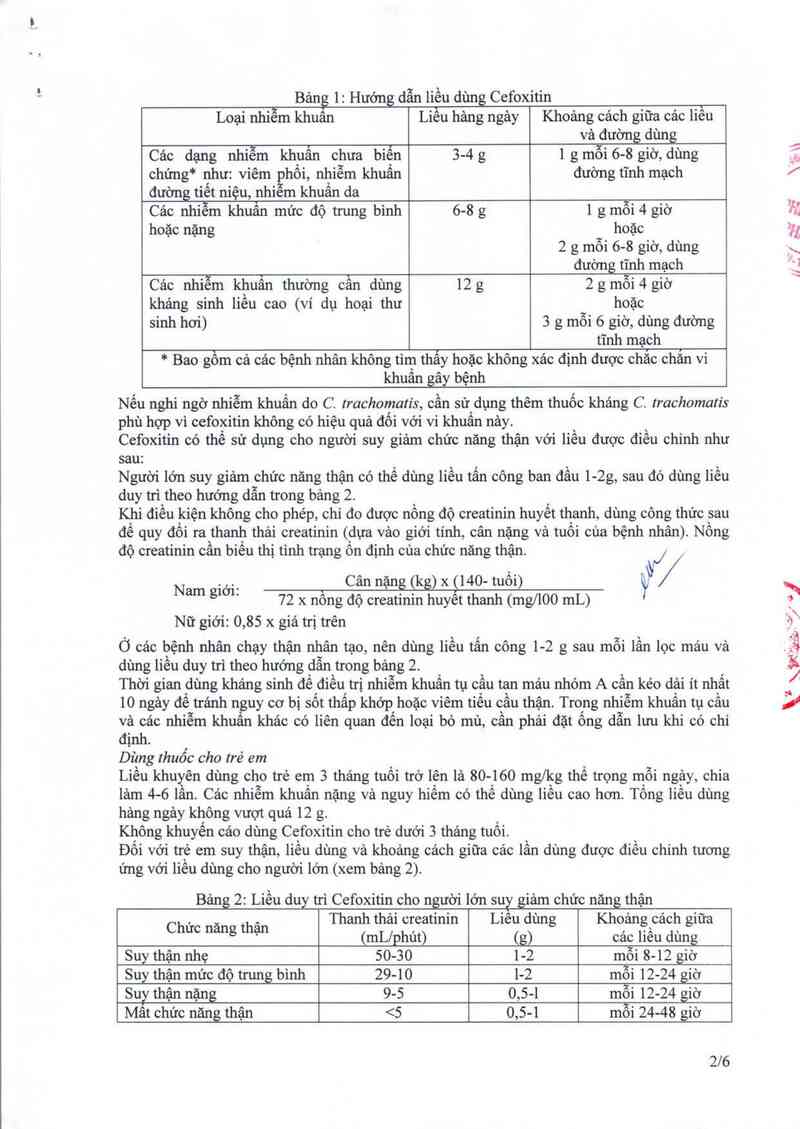
Bảng 1: Hướng dẫn liều dùng Cefoxitin
Loại nhiễm khuẩn Liễu hảng ngảy Khoảng cách giữa cảc liều
vả đường dùng
Các dạng nhiễm khuấn chưa biến 3—4 g 1 g mỗi 6-8 giờ, dùng
chứng* như: viêm phổi, nhiễm khuẩn đường tĩnh mạch
đường tiết niệu, nhiễm khuấn da
Cảc nhiễm khuẩn mức độ trung bình 6-8 g 1 g mỗi 4 giờ
hoặc nặng hoặc
2 g mỗi 6-8 giờ, dùng
đường tĩnh mạch
Các nhiễm khuẩn thường cẩn dùng 12 g 2 g mỗi 4 giờ
kháng sinh liều cao (ví dụ hoại thư hoặc
sinh hơi) 3 g mỗi 6 giờ, dùng đường
tĩnh mạch
* Bao gồm cả các bệnh nhân không tìm thấy hoặc không xảc định được chắc chắn vi
khuẩn L ybệnh
Nếu nghi ngờ nhiễm khuẩn do C trachomatís, cần sử dụng thêm thuốc kháng C. trachomatis
phù hợp vì cefoxitin không có hiệu quả đối với vi khuấn nảy.
Cefoxitin có thế sử dụng cho người suy giảm chức năng thận với liều được điều chỉnh như
sau:
Người lớn suy giảm chức năng thận có thể dùng liếu tấn công ban đầu 1-2g, sau đó dùng liếu
duy trì theo hướng dẫn trong bảng 2
Khi điều kiện không cho phép, chi đo được nồng độ creatinin huyết thanh, dùng công thức sau
để quy đổi ra thanh thải creatinin (dựa vảo giới tính, cân nặng và tuối của bệnh nhân). Nồng
độ creatinin cần biểu thị tình trạng ôn định cùa chức năng thận. Ụ/
` Cân nặng (kg) x g14o- tuối) i /
72 x nông độ creatinin huyêt thanh (mg/IOO mL)
Nữ giới: 0,85 x giá trị trên
Ở các bệnh nhân chạy thận nhân tạo, nên dùng liếu tấn công 1-2 g sau mỗi lần lọc máu và
dùng liếu duy trì theo hướng dẫn trong bảng 2.
Thời gian dùng khảng sinh để điều trị nhiễm khuấn tụ cầu tan mảu nhóm A cần kéo dải ít nhất
10 ngảy để tránh nguy cơ bị sốt thấp khớp hoặc viêm tiều cầu thận. Trong nhiễm khuẩn tụ cầu
và các nhiễm khuấn khảo có liên quan đến loại bỏ mủ, cần phải đặt ong dẫn lưu khi có chi
đinh.
Dùng thuốc cho trẻ em
Liều khuyên dùng cho trẻ em 3 tháng tuổi trở lên là 80- 160 mg/kg thể trọng mỗi ngảy, chia
lảm 4— 6 lần. Cảo nhiễm khuấn nặng và nguy hiểm có thể dùng liều cao hơn. Tổng liều dùng
hảng ngây không vượt quá 12 g
Không khuyến cảo dùng Cefoxitin cho trẻ dưới 3 thảng tuổi.
Đối với trẻ em suy thận, liều dùng và khoảng cảch giữa các lần dùng được điều chinh tương
ứng với liều dùng cho người lởn (xem bảng 2).
Nam giới:
Bảng 2: Liều duy trì Cefoxitin cho người lớn suy giảm chức năng thận
, … Thanh thải creatinin Liêu dùn Khoản cách iữa
Chưc năng thạn (mL/phút) (g) g các Ễều dùngg
Suy thận nhẹ so-3o 1-2 mỗi 8-12 giờ
Suy thận mức độ trung bình 29…1o 1-2 mỗi 12-24 giờ
Suy thận nặng 9-5 0,5-l mỗi 12-24 giờ
Mẫt chức năng thận Jeu
Tương tác thuốc— xét nghiệm cận lâm sảng
Cũng như cephalothin, nông độ cao cefoxitin (>100 microgam/ml) có thể ảnh hưởng đển kết
quả định lượng creatinin trong máu và nước tiểu bằng phản ứng Jaffé, lảm tãng nồng độ
creatinin gây sai lệch kết quả. Bệnh nhân không nên lấy mẫu mảu để xét nghiệm creatinin
trong vòng 2 giờ sau khi dùng cefoxitin.
Nồng độ cao cefoxitin trong nước tiểu có thể ảnh hướng đến xét nghiệm 17- hydroxy—
corticosteroid trong nước tiếu bằng phản ứng Porter-Silber, lảm tăng nông độ 17— hydroxy-
corticosteroid gậy sai lệch kết quả.
Cefoxitin có thể gây phản ứng dương tính giả khi xét nghiệm đường trong nước tiểu bằng
CLTNITEST
DÙNG THUỐC cno PHỤ NỮ có THAI VÀ cno CON BỦ
Phụ nữ có thai
Các nghiên cứu về sinh sản được tiến hảnh trên chuột cống và chuột nhắt vởi liều tiêm gấp 1-
7, 5 lần liếu tối đa khuyên dùng cho người, cho thấy thuốc không gây quái thai hoặc gây độc
cho thai mặc dù có sự giảm nhẹ trọng lượng cùa chuột con.
Tuy nhiên, chưa có các nghiên oứu đầy đủ và có kiếm soát về việc dùng thuốc cho phụ nữ có
thai Do các nghiên oứu trên động vật không phải lủc nảo cũng cho đảp ứng tương tự trên
người nên chi dùng thuốc nảy cho phụ nữ có thai khi thực sự cân thiết.
Trên thỏ, cefoxitin gây tăng tần xuất sảy thai và tử vong ở thỏ mẹ. Điều nảy không được coi là
tác đụng gây quải thai nhưng được cho là hậu quả của sự quá nhạy cảm của thỏ đối với sự
thay đổi hệ vi sinh vật ở đường ruột do sử dụng khảng sinh.
Phụ nữ cho con bú
Cefoxitin được tiết vảo sữa mẹ với nồng độ thấp. Thận trọng khi dùng cefoxitin cho phụ nữ
đang cho con bủ.
ẢNH HƯỚNG ĐẾN KHẢ NĂNG LÁI XE VÀ VẬN HÀNH MÁY MÓC ịÙf”
Thuốc không ảnh hưởng đến khả năng lải xe và vận hảnh mảy móc.
TÁC DỤNG KHÔNG MONG MUÔN
Nhìn chung cefoxitin được dung nạp tốt. Tảo dụng không mong muốn thường gặp nhất là
phản ứng tại chỗ sau khi tiêm tĩnh mạch. Các tảo dụng phụ khảo được xêp vảo ioại xảy ra
không thường xuyên.
Phản ứng tại chỗ. Viêm tĩnh mạch huyết khối xảy ra sau khi tiêm tĩnh mạch.
Phán ửng dị ứng. Phảt ban (bao gôm cả viêm tróc da và hoại tử da nhiễm độc), mảy đay, đò
da, ngứa, tăng bạch cầu ưa eosin, sốt, khó thở và oảo phản ứng dị ứng khác bao gôm phản’ ưng
phản vệ, viếm thận kê và phù mạch đã được bảo cảo.
Tim mạch Hạ huyết ảp
Tiêu hoá: Tiêu chảy bao gồm cả viêm đại trảng giả mạc có thể xuất hiện trong hoặc sau thời
gian điều trị bằng kháng sinh. Buồn nôn vả nôn hiếm khi xảy ra.
Thần kinh cơ. Có thế lảm nặng thêm bệnh nhược cơ năng.
Máu Tăng bạch cầu ưa eosin, giảm bạch cầu hạt bao gồm giảm bạoh cằu hạt— huyết giảm
bạch câu trung tính, thiếu mảu bao gôm oả thiếu mảu tan huyết, giảm tiểu cầu, và suy tủy. Có
thể xảy ra kết quả dương tính với test Coombs trực tiếp ở một sô bệnh nhân, đặc biệt ở bệnh
nhân tăng urê huyết.
Chửc năng gan. Tăng thoảng qua nồng độ SGOT, SGPT, LDH trong máu và alkaline
phosphatase trong mảu; vảng da dã được bảo cảo
Chức năng thận. Tăng nông độ creatinin huyết thanh vả/hoặc urê mảu đã được bảo cảo. Cũng
như với cảc cephalosporin, suy thận cấp hiếm khi xảy ra. Rất khó để đảnh giả ảnh hưởng của
Cefoxitin đối với sự thay đổi kểt quả test thử chức năng thận vì thường xuyên có cảc yêu tố
khác dẫn đến nỉtơ huyết ngoải thận hoặc suy giảm chức năng thận.
5/6
Ao -.f—xc ơ.…\
Ngoài các tảc dụng không mong muốn kể trên được bảo cảo xảy ra ở bệnh nhân điếu trị bằng
Cefoxitin, các tảo dụng không mong muốn sau được báo cảo xảy ra đối với cảc kháng sinh
cephalosporin:
Mảy đay, ban đó đa dạng, hội chứng Stevens- Johnson, phản ứng giống bệnh huyết thanh, đau
bụng, viêm đại trảng, suy thận, nhiễm độc thận, gây kết quả dương tính giả khi xét nghiệm
glucose trong nước tiếu, suy giảm chức năng gan bao gôm ứ mật, tăng nông dộ bilirubin,
thiếu máu bât sản, xuất huyết, kéo dải thời gian prothrombin, giảm toản thế huyết cầu, mất
bạch cầu hạt, bội nhiễm, viêm âm đạo bao gồm cả nhiễm nâm candida am đạo.
Một số cephalosporin được cho là tảc nhân gây các cơn động kinh, đặc biệt ở những bệnh
nhân suy thận mã không giảm liều. Nếu xảy ra cơn động kinh do dùng thuốc, cân ngừng sử -›`Ề ,
dụng. Nếu có chỉ định, cân dùng cảc thuốc chống co giật. "
* T hong báo cho bác s: 'những tác dụng không mong muốn gặp phải khi sử dụng thuốc.
QUÁ LIÊU
Chưa có thuốc giải độc đặc hiệu, cần ảp dụng các biện pháp hỗ trợ thông thường. Ở những
bệnh nhân suy thận, Cefoxitin có thế được loại bỏ bởi quá trình lọc máu.
TỈNH TƯỜNG HỢP VÀ ĐỘ ÒN ĐỊNH
Dung dịch chứa lg Cefoxitin trong 10 mL nước cất pha tiêm vô khuấn, dung dịch tiêm Natri
Clorid 0, 9% hoặc dung dịch tiêm Dextrosc 5% ổn định trong 6 giờ khi bảo quản ở nhiệt độ
phòng và trong 1 tuần khi bảo quản lạnh (dưới 5°C).
Các dung dịch trên có thể tiếp tục được pha loãng trong 50-1000 mL một trong các dung môi
sau và giữ được hoạt lực trong 18 giờ tiếp theo khi bảo quản ở nhiệt độ phòng hoặc 48 giờ
tiếp theo khi được bảo quản lạnh:
— Dung dịch tiêm Natri clorid 0,9%.
- Dung dịch tiêm Dextrosc 5% hoặc 10% ỷị~
- Dung dịch tiêm Dextrosc 5% và Natri clorid 0,9%
- Dung dịch tiêm Dextrosc 5% và Natri clorid 0,2% hoặc 0,45%
- Dung dịch tiêm Ringer Lactat
- Dung dịch tiêm Dextrose 5% trong Ringer Lactat
- Dung dịch tiêm Natri Bicarbonat 5%
- Dung dịch tiêm Natri Lactat Ml6
Mannitol 5% và 10%
Sau thời gian trên, phần dung dịch chưa dùng hết phải được hủy bỏ.
BẢO QỤẢN: Trong hộp kín, nơi khô, ở nhiệt độ dưới 30°C, tránh ánh sáng '
HAN DÙNG: 24 tháng kế từ ngảy sản xuất. 1
* Không dùng thuốc qua' thời hạn sử dụng. 'ắ
QUY CÁCH ĐÓNG GÓI. Lọ lg, hộp 1 lọ. ;_1
Sản xuất bởi: 3
CÔNG TY TNHH PHIL INTER PHARMA \
Số 20, Đại lộ Hữu Nghị, KCN Việt Nam-Singapore, Thuận An, Bình Dương
6/6
Rx Prescription drug
Keep out of reach of children.
Read the package insert carefully before using.
F or any more information, please consult your doctor.
SCUBIG
Visa No.: ..........
COMPOSITION: Each via] contains:
Active ingredients: Cefoxitin sodium equivalent to Cefoxitin ......................... 1 g
DOSAGE FORM: Powder for injection
PHARMACOLOGY
Cefoxitin is a semi-synthetic, broad-spectrum cephalosporin. The bactericidal action of
cefoxitin results from inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Cefoxitin has in vitro activity against a
wide range of gram-positive and gram-negative organisms. The methoxy group in the 7u
position provides cefoxitin with a high degree of stability in the presence of beta-lactamases,
both penicillinases and cephalosporinases, of gram-negative bacteria.
PHARMACOKINETIC
Following an intravenous dose of 1 gram, serum concentrations were 110 mcg/mL at
5 minutes, declining to less than 1 mcg/mL at 4 hours. The half-life after an intravenous dose
is 41 to 59 minutes. Approximately 85 percent of cefoxitin is excreted unchanged by the
kidneys over a 6-hour period, resulting in high urinary concentrations. Probenecid slows
tubular excretion and produces higher serum levels and increases the duration of measurable
serum concentrations.
Cefoxitin passes into pleural and joint fluids and is detectable in antibacterial concentrations
in bile.
INDICATIONS
T reatment:
Cefoxitin is indicated for the treatment of serious infections caused by susceptible strains of
the designated microorganisms in the diseases listed below.
- Lower respiratory tract infections, including pneumonia and lung abscess
- Urinary tract infections
— Intra-abdominal infections, including peritonitis and intra-abdominal abscess
- Gynecological infections, including endometritis, pelvic cellulitis, and pelvic
inflammatory disease
— Septicemia
- Bone and joint infections
- Skin and skin structure infections
Prevention:
Cefoxitin is indicated for the prophylaxis of infection in patients undergoing uncontaminated
gastrointestinal surgery, vaginal hysterectomy, abdominal hysterectomy, or cesarean section.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE
Treatment
Adults
The usual adult dosage range is 1 gram to 2 grams every six to eight hours. Dosage should be
determined by susceptibility of the causative organisms, severity of infection, and the
condition of the patient (see Table ] for dosage guidelines).
1/6
%
.AAM-n
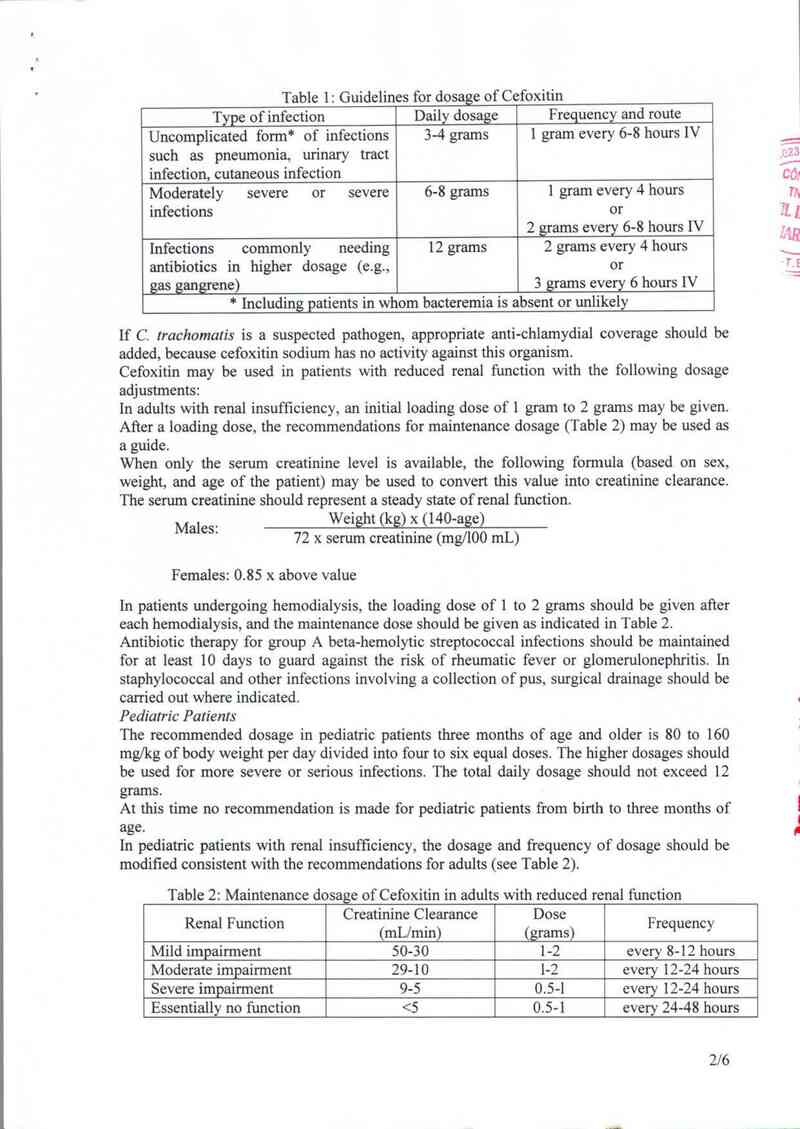
Table l: Guidelines for dogggof Cefoxitin
Type of infection Daily dosage Frequency and route
Uncomplicated form* of infections 3-4 grams ] gram every 6-8 hours IV
such as pneumonia, urinary tract
infection, cutaneous infection
Moderater severe or severe 6-8 grams 1 gram every 4 hours
infections or
2 grams every 6—8 hours IV
Infections commonly needing 12 grams 2 grams every 4 hours
antibiotics in higher dosage (e.g., or
as an ene) 3 grams every 6 hours IV
* Including patients in whom bacteremia is absent or unlikely
If C. trachomatis is a suspected pathogen, appropriate anti-chlamydial coverage should be
added, because cefoxitin sodium has no activity against this organism.
Cefoxitin may be used in patients with reduced renal f1mction with the following dosage
adjustments:
In adults with renal insufficiency, an initial loading dose of ] gram to 2 grams may be given.
After a loading dose, the recommendations for maintenance dosage (Table 2) may be used as
a guide.
When only the serum creatinine level is available, the following formula (based on sex,
weight, and age of the patient) may be used to convert this value into creatinine clearance.
The serum creatinine should represent a steady state of renal function.
Males Weight (kg) x (140-age)
' 72 x serum creatinine (mgllOO mL)
Females: 0.85 x above value
In patients undergoing hemodialysis, the loading dose of 1 to 2 grams should be given after
each hemodialysis, and the maintenance dose should be given as indicated in Table 2.
Antibiotic therapy for group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections should be maintained
for at least 10 days to guard against the risk of rheumatic fever or glomerulonephritis. In
staphylococcal and other infections involving a collection of pus, surgical drainage should be
carried out where indicated.
Pediatric Paíients
The recommended dosage in pediatric patients three months of age and older is 80 to 160
mg/kg of body weight per day divided into four to six equal doses. The higher dosages should
be used for more severe or serious infections. The total daily đosage should not exceed 12
grams.
At this time no recommendation is made for pediatric patients from binh to three months of
age.
In pcdiatric patients with renal insufficiency, the dosage and frcquency of dosage should be
modified consistent with the recommendations for adults (see Table 2).
Table 2: Maintenance dosage of Cefoxitin in adults with reduced renal function
Renal Function Creatinine Ciearance Dose Frequency
(mL/mm) (grams)
Mild impairment 50—30 1-2 every 8-12 hours
Moderate impairment 29—10 1-2 every 12-24 hours
Severe impairment 9—5 0.5-1 every 12-24 hours
Essentially no function <5 0.5-1 every 24—48 hours
2/6
zsii
x~r-
o
9
TAI
.t:/ =ỉã ỉĩ
Prevention
Eft`ective prophylactic use depends on the time of administration. Cefoxitin usually should be
given one—half to one hour before the operation, which is sufflcient time to achieve effective
levels in the wound during the procedure. Prophylactic administration should usually be
stopped within 24 hours since continuing administration of any antibiotic increases the
possibility of adverse reactions but, in the majority of surgical procedures, does not reduce the
incidence of subsequent infection.
For prophylactic use in uncontaminated gastrointestinal surgery, vaginal hysterectomy, or
abdominal hysterectomy, the following doses are recommended:
Adults: 2 grams administered intravenously just prior to surgery (approximately one—half to
one hour before the initial incision) followed by 2 grams every 6 hours after the first dose for
no more than 24 hours.
Pediatn'c patients (3 months and older): 30 to 40 mg/kg doses may be given at the times
designated above.
Cesarean section patients:
For patients undergoing cesaxean section, either a single 2 gram dose administered
intravenously as soon as the umbilical cord is clamped OR a 3-dose regimen consisting of 2
grams given intravenously as soon as the umbilical cord is clamped followed by 2 grams 4
and 8 hours after the initial dose is recommended.
PREPARA TION OF SOL UTION
Table 3 is provided for convenience in constituting Cefoxitin for intravenous administration.
Table 3: Pre aaxation of Solution for Intravenous Administration
Strength Amount of diluent Approximate Approximate average
to be added withdrawable concentration
(mL)** volume (mL) (mẵmL)
] gram vial 10 10.5 95
** Shake to dissolve and let stand until clear.
Vial of 1 gram should be constituted with 10 mL of Sterile Water for Injection, 0.9 percent
Sodium Chloride Injection, or 5 percent Dextrosc Injection. These primary solutions may be
further diluted in 50 to 1000 mL of the following diluents:
- 0.9 percent Sodium Chloride Injection
- 5 percent or 10 percent Dextrosc Injection
- 5 percent Dextrosc and 0.9 percent Sodium Chloride Injection
- 5 percent Dextrosc Injection with 0.2 percent or 0.45 percent saline solution
- Lactated Ringer’s Injection
- 5 percent Dextrosc in Lactated Ringer’s Injection
- 5 percent Sodium Bicarbonate injection
- M/6 sodium lactate solution
— Mannitol 5% and 10%
A DMINISTRA TION
Cefoxitin may be administered intravenously after constitution.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration
prior to administration whenever solution and container permit.
For intermittent intravenous administration, a solution containing l gram in 10 mL of Sterile
Water for Injection can be injected over a period of three to five minutes. Using an infi.tsion
system, it may also be given over a longer period of time through the tubing system by which
the patient may be receiving other intravenous solutions. However, during infusion of the
solution containing Cefoxitin, it is advisable to temporarily discontinue administration of any
other solutions at the same site.
3/6
I—A ..-
For the administration of higher doses by continuous intravenous infusion, a solution of
Cefoxitin may be added to an intravenous bottle containing 5 percent Dextrosc Injection, 0.9
percent Sodium Chloride Injection, or 5 percent Dextrosc and 0.9 percent Sodium Chloride
Injection.
Solutions of Cefoxitin, like those of most beta—lactam antibiotics, should not be added to
aminoglycoside solutions (e.g., gentamicin sulfate, tobramycin sulfate, amikacin sulfate)
because of potential interaction. However, Cefoxitin and aminoglycosides may be
administered separater to the same patient.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Cefoxitin is contraindicated in patients who have shown hypersensitivity to cefoxitin and the
cephalosporin group of antibiotics.
WARNINGS
Before therapy with Cefoxitin is instituted, careful inquiry should be made to determine
whether the patient has had previous hypersensitivity reactions to cefoxitin, cephalosporins,
penicillins, or other drugs. This product should be given with caution to penicillin-sensitive
patients. Antibiotics should be administered with caution to any patient who has demonstrated
some form of allergy, particularly to drugs. If an allergic reaction to Cefoxitin occurs,
discontinue the drug. Serious hypersensitivity reactions may require Epinephrine and other
emergency measures.
Pseudomembranous colitis has been reported with nearly all antibacterial agents, including
cefoxitin, and may range in severity from mild to life threatening. Therefore, it is important to
consider this diagnosis in patients who present with diarrhea subsequent to the administration
of antibacterial agents.
Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon and may permit
overgrowth of clostridia. Studies indicate that a toxin produced by Clostridium difflcile is one
primary cause of “antibiotic associated colitis”.
After the diagnosis of pseudomembranous colitis has been established, appropriate therapeutic
measures should be initiated. Mild cases of pseudomembranous colitis usually respond to
drug discontinuation alone. In moderate to severe cases, consideration should be given to
management with fluids and electrolytes, protein supplementation, and treatment with an
antibacterial drug clinically effective against Clostridium difiìcile colitis.
PRECAUTIONS
General
The total daily dose should be reduced when Cefoxitin is administered to patients with
transient or persistent reduction of urinary output due to renal insufficiency because high and
prolonged serum antibiotic concentrations can occur in such individuals from usual doses.
Antibiotics (including cephalosporins) should be prescribed with caution in individuals with a
history of gastrointestinal disease, panicularly colitis.
As with other antibiotics, prolonged use of Cefoxitin may result in overgrowth of
nonsusceptible organisms. Repeated evaluation of the patient’s condition is essential. If
superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate measures should be taken.
Laboratory Tests
As with any potent antibacterial agent, periodic assessment of organ system functions,
including renal, hepatic, and hematopoietic, is advisable during prolonged therapy.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed with cefoxitin to evaluate carcinogenic
or mutagenic potential. Studies in rats treated intravenously with 400 mg/kg of cefoxitin
(approximately three times the maximum recommended human dose) revealed no effects on
fertility or mating ability.
4/6
.: \ửJ ln..'
Pediatric Use
Safety and efflcacy in pediatric patients from binh to three months of age have not yet been
established. In pediatric patients three months of age and older, higher doses of Cefoxitin
have been associated with an increased incidence of eosinophilia and elevated SGOT.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Increased nephrotoxicity has been reported following concomitant administration of
cephalosporins and aminoglycoside antibiotics.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
As with cephalothin, high concentrations of cefoxitin (>100 micrograms/ml) may interfere
with measurement of serum and urine creatinine levels by the Jaffé reaction, and produce
false increases of modest degree in the levels of creatinine reported. Serum samples from
patients treated with cefoxitin should not be analyzed for creatinine if withdrawn within 2
hours of drug administration.
High concentrations of cefoxitin in the urine may interfere with measurement of urinary 17-
hydroxy-corticosteroids by the Porter-Silber reaction, and produce false increases of modest
degree in the levels reported.
A false-positive reaction for glucose in the urine may occur. This has been observed with
CLINITEST reagent tablets.
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION
Pregnancy
Reproduction studies performed in rats and mice at parenteral doses of approximately one to
seven and one-half times the maximum recommended human dose did not reveal teratogenic
or fetal toxic effects, although a slight decrease in fetal weight was observed.
There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because
animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be
used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
In the rabbit, cefoxitin was associated with a high incidence of abortion and maternal death.
This was not considered to be a teratogenic effect but an expected consequence of the rabbit’s
unusual sensitivity to antibiotic-induced changes in the population of the microfiora of the
intestine.
Nursing Mothers
Cefoxitin is excreted in human milk in low concentrations. Caution should be exercised when
Cefoxitin is administered to a nursing woman.
EFFECT TO THE ABILITY OF DRIVIN G CAR AND OPERATING MACHINE:
No effect.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Cefoxitin is generally well tolerated. The most common adverse reactions have been local
reactions following intravenous injection. Other adverse reactions have been encountered
infrequently.
Local Reactions: Thrombophlebitis has occurred with intravenous administration.
Allergic Reactions: Rash (including exfoliative dermatitis and toxic epidermal necrolysis),
urticaria, fiushing, pruritus, eosinophilia, fever, dyspnea, and other allergic reactions
including anaphylaxis, interstitial nephritis and angioedema have been noted.
Cardiovascular: Hypotension.
Gastrointestinal: Diarrhea, including documented pseudomembranous colitis which can
appear during or after antibiotic treatment. Nausea and vomiting have been reported rarely.
Neuromuscular: Possible exacerbation of myasthenia gravis.
Blood: Eosinophilia, leukopenia including granulocytopenia, neutropenia, anemia, including
hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and bone marrow depression. A positive direct Coombs
test may develop in some individuals, especially those with azotemia.
5/6
Liver F unction: Transient elevations in SGOT, SGPT, serum LDH, and serum alkaline
phosphatase; and jaundice have been reported.
Renal Function: Elevations in serum creatinine and/or blood urea nitrogen levels have been
observed. As with the cephalosporins, acute renal failure has been reported rarely. The role of
Cefoxitin in changes in renal function tests is difflcult to assess, since factors predisposing to
prerenal azotemia or to impaired renal function usually have been present.
In addition to the adverse reactions listed above which have been observed in patients treated
with Cefoxitin, the following adverse reactions and altered laboratory test results have been
reported for cephalosporin class antibiotics:
Urticaria, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, serum sickness-like reactions,
abdominal pain, colitis, renal dysfunction, toxic nephropathy, false-positive test for urinary
glucose, hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis, elevated bilirubin, aplastic anemia,
hemorrhage, prolonged prothrombin time, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis, superinfection,
vaginitis ìncluding vaginal candidiasis.
Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients
with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced. If seizures associated with drug
therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if
clinically indicated.
Inform your doctor in case of an y adverse reactions related to drug use.
OVERDOSE
Symptoms and treatrnent: Other than general supportive treatment, no specific antidote is
known. Cefoxitin can be eliminated by dialysis in patients with renal insufficiency.
COMPATIBILITY AND STABILITY
Cefoxitin constìtuted to 1 gram/ 10 mL with Sterile Water for Injection, 0.9 percent Sodium
Chloride Injection, or 5 percent Dextrosc Injection, maintains satisfactory potency fo; 6 hours
at room temperature or for one week under refrigeration (below 5°C).
These primary soiutions may be further diluted in 50 to 1000 mL of the following diluents
and maintain potency for an additional 18 hours at room temperature or an additional 48 hours
under refrigeration:
— 0.9 percent Sodium Chloride Injection
- 5 percent or 10 percent Dextrosc Injection
- 5 percent Dextrosc and 0.9 percent Sodium Chloride Injection .
- 5 percent Dextrosc Injection with 0.2 percent or 0.45 percent saline solution `
- Lactated Ringer’s Injection
- 5 percent Dextrosc in Lactated Ringer’s Injection
~ 5 percent Sodium Bicarbonate injection
- M/6 sodium lactate solution
- Mannitol 5% and 10%
After the periods mentioned above, any unused solutions should be discarded.
STORAGE: In a hermetíc container, dry place, below 300C , protect from light.
SHELF—LIFE: 24 months from manufacturing date.
Do not use ị/the drug is out ofdate.
PACKAGE: lg/vial. Box of 01 vial.
Manufactured by
PHIL INTER PHARMA CO., LTD
No.20, Huu Nghi Bld., Vietnam—Singapore Industrial P
rặzỉìẶ_xgịỉịìigqcnử LƯỢ '
ng… ;I` . \ J/`"ồ ,
» TY
a”… ,Ị TU ,
;; ~r ,….-
~a PrJỉ Fu
x;gÀ mu…
\\,f-ế'ềsởg/x. /
\»; ắt ; f1MsươN G LAN PHÓ cuc muòne
# %… %
` , _, /
+ "Lưu ý những sản phẩm đăng trên website thuộc loại thực phẩm chức năng: những sản phẩm này không phải là thuốc và không có tác dụng thay thế thuốc chữa bệnh"
+ Dùng thuốc theo chỉ định của Bác sĩ
+ Đọc kỹ hướng dẫn sử dụng trước khi dùng